Torque exhaust manifold nuts
A loose manifold could alter air/fuel ratio and cause an increase in emissions and/or poor driveability.
Valves
The valve clearance should be check and, if necessary, adjusted every 30,000 miles (48,000 km).
Air cleaner
Replace the air cleaner cartridge with a new one every 30,000 miles (48,000 km). The cartridge should be replaced more often when driving under dirty and dusty conditions, The filter cannot be cleaned and, therefore, should always be replaced with a new one.
Vacuum fittings, hoses and connections
Unstable idle, misfiring, or poor emission control is often caused by leaking vacuum hoses or connections. Check hoses and connections on distributor vacuum unit, connections on heater control servo systems and hydraulic brake servo.
Checking and adjusting idle speed
Your Volvo is equipped with an electronically-controlled idle speed system that requires no checking or adjustment.
Fuel system cap, tank and lines, and connections
The effectiveness of the fuel system to contain hydrocarbons is dependent largely on a leakfree system. Check for proper sealing of gasoline filler cap which contains "0" ring-type seals. Check all evaporative hoses in vehicle for tightness. Check fuel lines under vehicle and repair if necessary.
Fuel (line) filter
The fuel line filter is located next to the fuel pump. This filter should be replaced every 60,000 miles (96,000 km). The filter is replaced as one complete unit.
Replace more frequently if contaminated fuel is introduced into the tank (or if there is reason to suspect that this has occurred).
Timing gear belt
The timing gear belt should be adjusted at the 600-1,200 mile (1000-2000 km) inspection. We recommend that the timing gear belt be replaced every 50,000 miles (80,000 km).
pg. 104 Servicing |

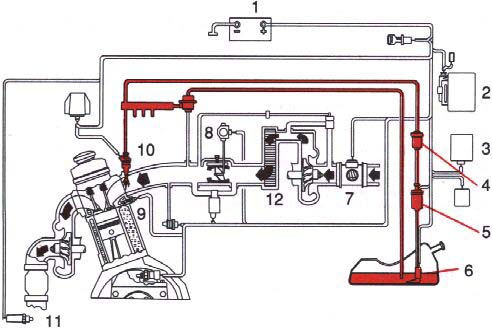
1 Battery
2 Injection control unit
3 Ignition control unit
4 Fuel filter
5 Fuel pump
6 Fuel feed pump
7 Air mass meter*
8 Throttle switch
9 Temperature sensor
10 Injector
11 Oxygen sensor
12 Intercooler (Turbo models)
* Pressure meter on certain models
Fuel system
The fuel injection system is all-electronic and microprocessor-controlled. It can continually compensate for variations in engine load, speed and temperature to give the best economy and power. A mass air flow sensor or a pressure meter on certain models, measures the inducted air. In this way the system can make instantaneous adjustments for changes in air temperature or density, thus always assuring the best economy with the lowest possible exhaust emissions.
Lambda-sond (oxygen sensor)
system
This is an emission control system designed to reduce emissions and improve fuel economy. The heated oxygen sensor monitors the composition of the exhaust gases leaving the engine. The exhaust gas analysis is fed into an electronic control module. This adjusts the air-fuel ratio to provide optimum conditions for combustion and efficient reduction of the three major pollutants (hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide and nitrous gases) by a 3-way catalytic converter.
pg. 105 Servicing (cont.) |
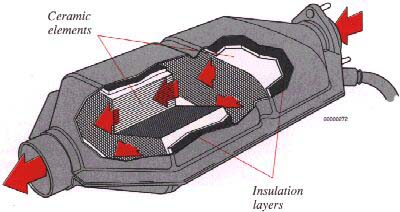
Catalytic Converter
This is a supplementary device in the exhaust system, designed to clean exhaust gases. This device is mainly a container with a ceramic material insert, designed to let the exhaust gases pass through channels in the insert. The channel walls are covered by a thin layer of platinum-palladium. These metals act as catalysts, permitting a chemical action to occur without actually taking part in it.
The emission (CO, HC, NOx) content will increase if the three-way catalytic converter is damaged. Lambda-sond equipped vehicles use Catalytic Converters containing platinum and rhodium.
Torque Catalytic Converter mounting bolts
The Catalytic Converter mounting bolts should be torqued after the first 600-1,200 miles (1,000-2,000 km).
CAUTION:
|
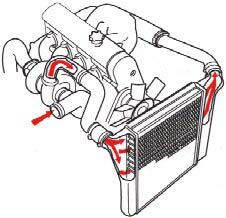
Intercooler
The B230F-Turbo engine employs a turbocompressor to force air into the engine inlet manifold and a charge air cooler to cool the compressed inlet air. The resulting increase in air flow raises pressure in the intake manifold by approx. 8 psi (over atmospheric pressure) and engine power output by approx. 46 horsepower over that developed by the normally-aspirated engine.
The intercooler (which resembles a radiator) is located between the turbocompressor and inlet manifold.
pg. 106 Servicing (cont.) |
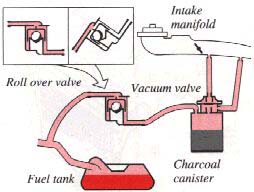
Evaporative control system
The 740 is equipped with a gas-evaporative control system, which prevents gasoline fumes from being released into the atmosphere. The system is comprised of an expansion chamber in the fuel tank, and a charcoal canister with built-in vacuum valve under the left-front wheel housing.
The components are interconnected by hoses which channel fuel vapor from the gas tank to the charcoal filter, where it is stored until the engine is started and then drawn into the engine's fuel-induction system.
Crankcase ventilation
The engine is equipped with positive crankcase ventilation which prevents crankcase gases from being released into the atmosphere. Instead, the crankcase gases are admitted to the intake manifold and cylinders.
PCV system
The PCV nipple in the intake manifold should be removed and inspected every 60,000 miles (96,000 km).
Check/replace hoses at the same time.
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR)
This system operates by returning some of the exhaust gases to the engine to be recombusted: since this lowers the combustion temperature the amount of nitrogen oxides released into the atmosphere is reduced.
The EGR valve should be inspected at 12,000 miles (20,000 km) and thereafter cleaned every 24,000 miles (40,000 km).
pg. 107 Servicing (cont.) |
WARNING!
|
Replacing spark plugs
The spark plugs should be changed every 30,000 miles (48,000 km). However, city driving or fast highway driving may necessitate changing after 15,000 miles (24,000 km) of driving. When installing new plugs, be sure to fit the right type and use correct torque, see Specifications. When changing the plugs, check that the suppressor connectors are in good condition. Cracked or damaged connectors should be replaced.
When changing the spark plugs, clean the terminals and the rubber seals. If the car is driven on roads where salt is used during the winter, coat the cables with silicone.